Overview
Clean.Net uses SQL Server as its default database and leverages Entity Framework Core together with
the Repository Pattern for data access. Database schema management is fully automated through SQL
script-based migrations. These migrations are version-controlled and automatically executed during
each application startup. Each script is tracked using a dedicated SchemaVersions table
to
ensure idempotency—guaranteeing that no script is executed more than once. Because the migrations
are written as pure SQL scripts, they can also be manually executed against the database when
needed, providing flexibility and transparency in schema evolution.
First-Time Setup
When the application starts up for the first time, it will automatically set up the entire database
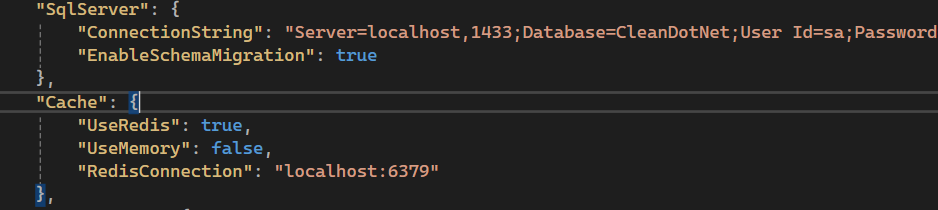
schema. Whether thats using the in-built database or your own database. You can control this setting
via the EnableSchemaMigration setting.
Adding New Migration Scripts
- Add a new SQL file in the
/src/Infrastructure/Persistence/Database/Migrationfolder - Name the file using the format:
NNNN_Description.sql, whereNNNNis a zero-padded number (e.g.,0001_InitialSetup.sql) - Set the build action on the script file to
Embedded Resource - Write your SQL changes in the script
- Scripts execute in filename order—prefixing with a number ensures correct sequence, especially when adding multiple scripts
- Once a script is deployed, never modify its content as it won't get executed again. Update the changes with a new script.
- Each script should be idempotent where possible
Manual Schema Migration Management
To disable automatic migrations, set the EnableSchemaMigration setting to false in the
appsettings.json file: